New Insight Into Cell Membranes Could Improve Drug Testing and Design
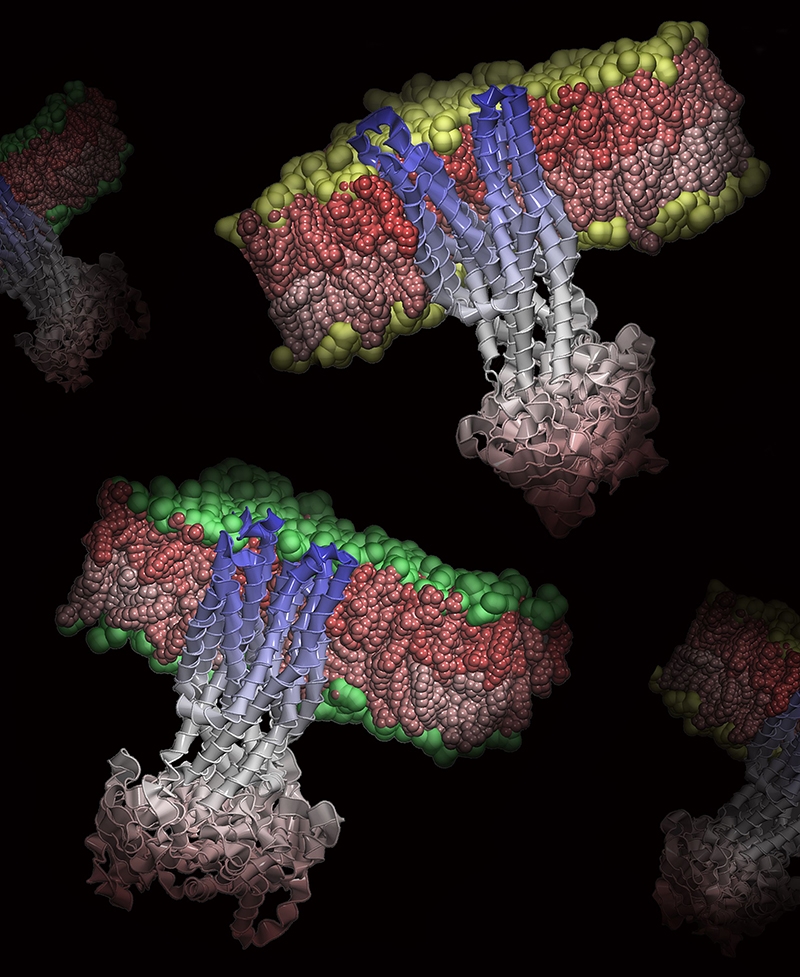
This image illustrates researchers' findings that the membrane proteins can be active, contributing to drug resistance, in cell membranes with one type of lipid composition (top), but inactive in membranes with a different lipid composition (bottom).
Research at the University of Arkansas on membrane proteins could lead to better development and testing of drugs. Chemistry researchers studied a type of membrane protein that expels drugs from a cell, contributing to drug resistance. They found that the lipid composition of the cell membrane has an effect on the behavior of these proteins, which should be taken into account when testing drugs that target membrane proteins. Their results are available open-access in the journal ACS Central Science.
Drug resistance, including bacterial resistance to antibiotics and cancer cells' resistance to chemotherapy, is a significant challenge for drug developers.
"Almost two-thirds of all drugs target membrane proteins," explained Mahmoud Moradi, assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry. "This research looks at how membrane proteins interact with the environment. If you ignore the fact that these proteins are dependent on their environment, you could end up with the wrong drugs."
Moradi and colleagues studied a type of membrane protein called multi-drug ABC exporters. These proteins transport substances, such as drugs, from the inside to the outside of cells, and they are responsible for both antibiotic resistance in bacteria and chemotherapy resistance in mammalian cells.
Using specially designed supercomputers supported by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health, the researchers performed molecular simulations to investigate how the lipid composition of a cell's membrane affects these proteins.
They found that these proteins remained inactive and didn't expel drugs in cell membranes with one type of lipid composition, called phosphocholine, or PC. However, the same proteins became active in cells with a different lipid composition, called phosphoethanolamine, or PE, allowing them to release drugs and making the cell resistant. Among the cell membranes composed of PE lipids, those containing one particular lipid type, called POPE, proved to be most effective in activating these proteins and thus most susceptible to drug resistance. Taking this information about the lipid environment into account could help researchers more effectively develop and test antibiotics and cancer treatments.
Contacts
Camilla Shumaker, director of science and research communications
University Relations
479-575-7422, camillas@uark.edu